How to engage with higher education providers
Businesses and HE providers can benefit from long-term, sustainable partnerships. The 13 member organisations of Go Higher West Yorkshire have collaborated to provide information on our website for businesses and employers, organised into three core strands which draw on our collective wealth of experience in business engagement across West Yorkshire:
Establishing contact with Higher Education Providers
Universities and colleges actively seek connections with businesses, and offer support and advice to make sure you get the most out of your relationship with them.
Most HE providers have business development teams who specialise in responding to queries and connecting external organisations with teams and departments across the entire institution. The contact details for these teams can be found below at the bottom of this webpage.
Your business might have an existing relationships with a university or college through individuals or departments, which can lead to long and fruitful partnerships which bring benefits to both parties. However, a connection built on a personal relationship can prove challenging as your contact may leave the institution, or might not have the knowledge or capacity to help the external organisation get the most out of the relationships.
Even if you already have an existing partnership with a particular individual, it might be helpful to get in touch with their employer engagement team for additional support if needed. This means you have an ongoing, supported contact within the institution, who understands your business and can let you know about opportunities, networks and funding which may be relevant to you.
Understanding Higher Education qualifications
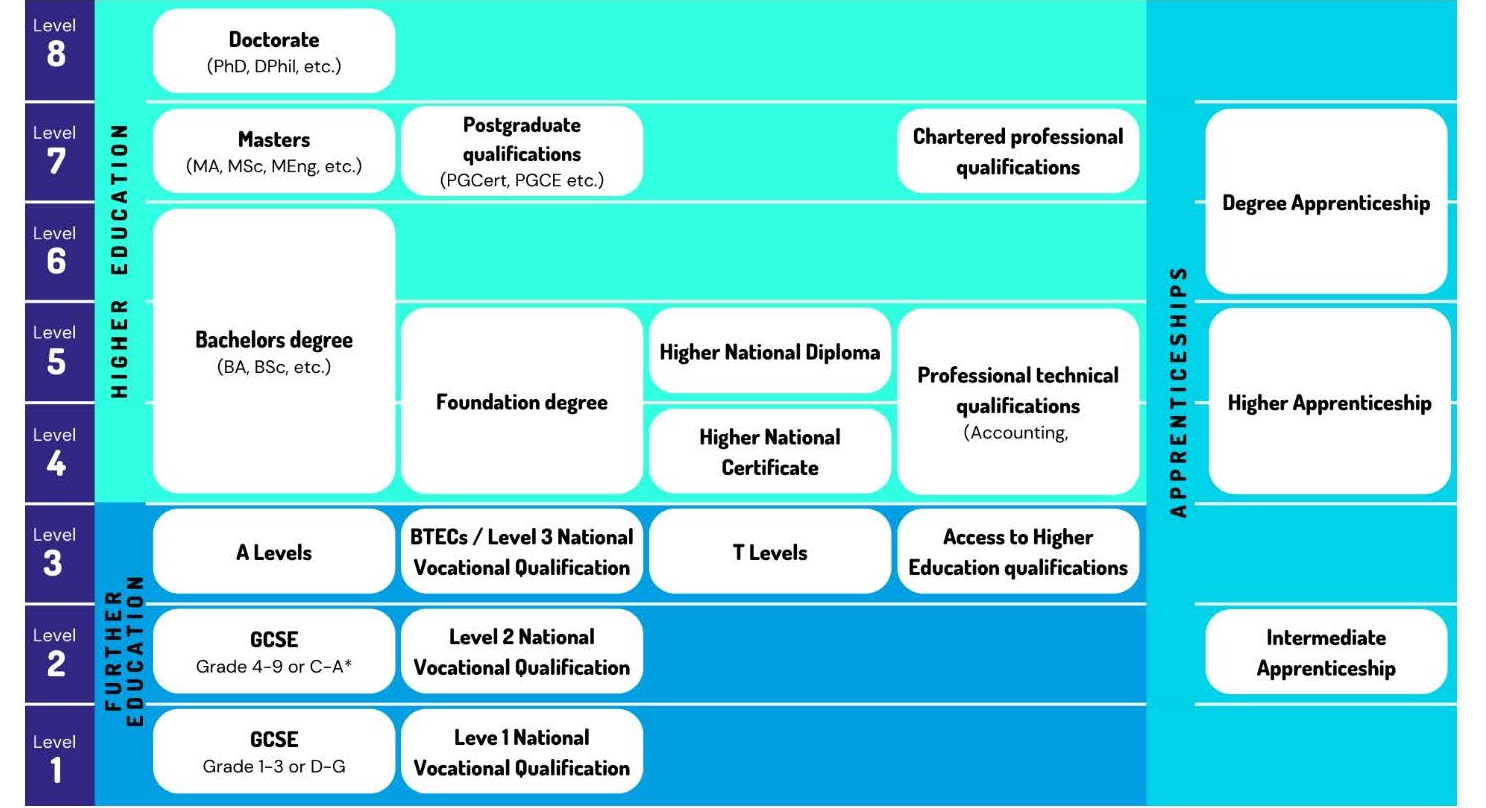
In England, Wales and Northern Ireland, there are eight different levels of education, which provide a framework to compare different courses and qualifications and understand how learners progress between them. The higher the level, the more advanced the qualification is.
Level 4 and above are considered higher-level qualifications. They are provided by: a University Centre within an FE college; a university; an approved training provider; or a conservatoire.
Bachelors or undergraduate degrees, which are generally studied over three years, are the most well-known higher-level qualification. There are nonetheless a range of alternatives that are becoming increasingly popular. These include Higher Apprenticeships, which mean you can earn while you learn, and Higher National Diplomas (HND), which prepare you for a particular career (e.g. business management).
Learners usually complete preceding levels before progressing to more advanced qualifications.
Qualifications can be grouped into vocational and academic:
- Vocational qualifications focus on practical application instead of theoretical knowledge. They can be offered in everything from animal care and manufacturing right through to management and health & safety.
- Academic programmes can offer work-based learning and industry insight through short-term opportunities, longer placements, or a year-in-industry (also known as a sandwich year).
Glossary of education terms
A Levels are subject-based academic qualifications usually studied by 16-19 year olds which can lead to university, further study, training, or work. Learners normally study three or more A levels over two years.
Access to Higher Education qualifications, sometimes called Access courses, are year-long Level 3 qualifications which prepare people without traditional qualifications for Higher Education study.
Apprenticeships are paid jobs where the learner receives both on-the-job training (80% of their time) and classroom-based learning (20% of their time), which leads to a nationally recognised qualification. Apprenticeships are offered between Level 2 up to Level 7.
BTECs are specialist work-related qualifications which combine practical and theoretical learning, usually studied up to Level 3. They’re usually studied at FE colleges and are designed for 16-19 year olds interested in a particular sector or industry but who aren’t yet sure what job they’d like to do.
Conservatoire (or Conservatory) is an institution that specialises in the performing arts. The programmes they offer focus on practical learning and performance.
Continuing Professional Development (CPD) is a type of education/training which combines new ideas, approaches, and techniques that will help individuals manage their own learning and growth.
Conversion courses are intensive, vocational postgraduate programmes which are the equivalent of a three-year undergraduate degree, usually compressed into one year of study.
Degree apprenticeships are apprenticeships which lead to a full undergraduate or master’s degree while the learner works in employment for 80% of the time. Degree apprenticeships take three to six years to complete, depending on the course level.
Equality, Diversity and Inclusion (EDI) are policies and approaches that aim to promote the fair representation, treatment and opportunity for all. It aims to remove prejudice and discrimination based on an individual or group of individual’s protected characteristics (e.g. age, race, sexual orientation).
Foundation degrees are combined academic and vocational qualifications which are the equivalent of two-thirds of Bachelor degree.
Further Education (FE) refers to any education after secondary school that is not an undergraduate or postgraduate degree.
Go Higher West Yorkshire (GHWY) is a partnership of 13 Higher Education Providers that works to achieve common goals on access to, success in and progression from HE for those from under-represented groups.
Graduate is a person who has successfully completed a course of study or training, especially a person who has been awarded an undergraduate or first academic degree.
Higher apprenticeships are apprenticeships which provide learners with an opportunity to gain Level 4 qualifications or above. A higher apprenticeship can take from one to five years to complete, and involve part-time study at a college, university, or training provider.
Higher Education takes places at universities and Further Education colleges and normally includes undergraduate and postgraduate study.
Higher Education (HE) in Further Education (FE) are HE courses such as Bachelor’s degrees, HNDs (Higher National Diploma), and professional technical qualifications which are studied in an FE college environment.
Higher Education Provider (HEP) is any institution that provides higher education qualifications, including universities, FE colleges with HE provision, and other approved organisations.
Higher National Certificate (HNC) is a vocational, work-related Higher Education qualification that prepares students for a particular job and/or career. It usually takes one year to complete and is equivalent to the first year of a degree.
Higher National Diploma (HND) is a vocational, work-related Higher Education qualification that prepares students for a particular job and/or career. It usually takes one year to complete and is equivalent to the first two years of a degree.
Internship is a time-limited period of (often paid) work experience offered by an employer to give students and graduates exposure to the workplace.
Masters degrees are academic qualifications usually studied after an undergraduate degree which take one year to complete.
Postgraduate diplomas (PGDip) and postgraduate certificates (PGCert) are qualifications at the same level of study as Masters degrees, but shorter.
Postgraduate qualifications are completed after an undergraduate degree (e.g. Masters, postgraduate certificate, PGCE).
Professional qualifications are vocational training courses that relate to a specific industry or career path. They can be studied directly after graduation, or aimed at professionals with several years of experience who are looking to develop their careers further. They are typically regulated and awarded by relevant professional bodies (not HE providers) although some are available through FE providers.
Sandwich year is a year that current students spend working within a business or other external organisation to gain industry experience, in a role aligned to their programme of study.
Specialist training providers are education providers who offer 60% or more of their courses in one or two subjects.
T Levels are a new, nationally-recognised qualification for 16 to 19-year-olds that takes two years to complete with a focus on vocational and technical learning. They’re equal to 3 A levels.
Top-up degrees convert an existing qualifications such as a HND or foundation degree into a full undergraduate degree through one year of study.
UK Research & Innovation is the national funding agency investing in science and research in the UK.
Undergraduate (or Bachelor) degrees are an academic step up from A-levels (or their equivalent) and usually take three years to complete. They are typically completed at a university or other higher education institution.
University Centres offer Higher Education courses in a Further Education setting.
Underrepresented groups are those less represented in one subset than in the general population e.g. men are underrepresented in the social care sector.